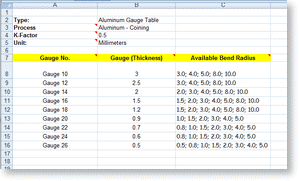
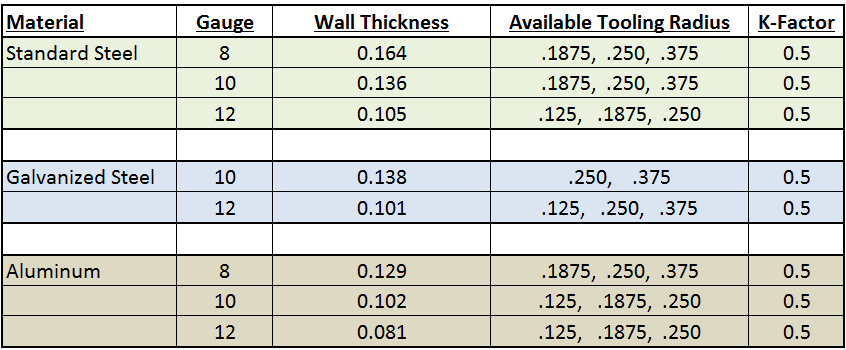
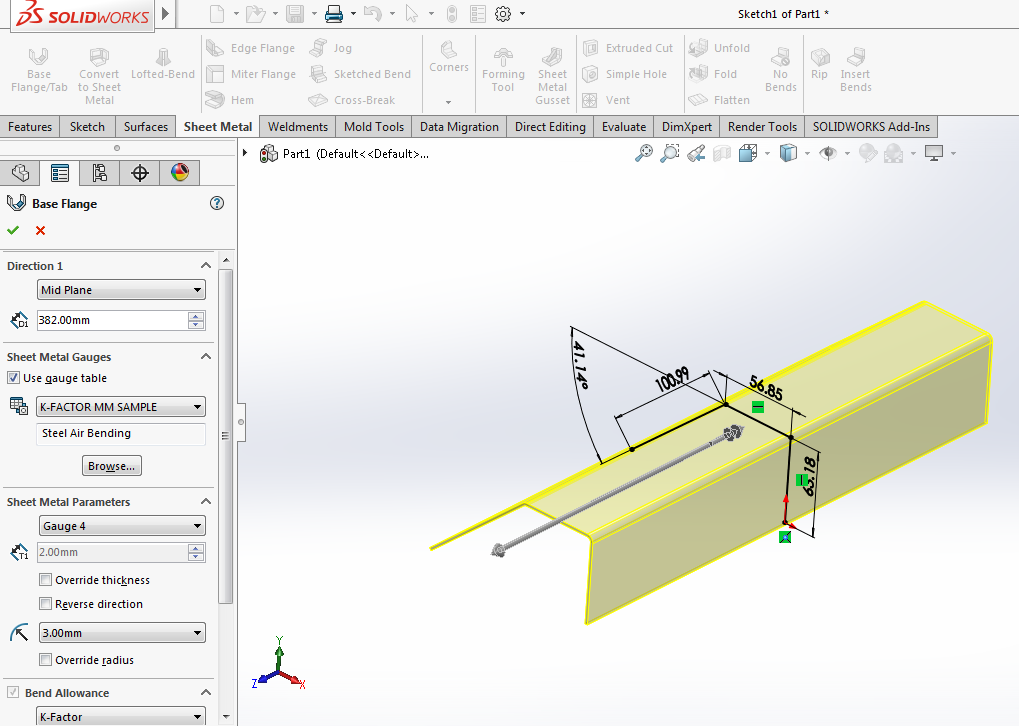
Sheet metal gauge is based on the weight of the sheet therefore a sheet of two different materials with the same thickness may have different gauge numbers.
Edit sheet metal material gauge.
When working with sheet metal a gauge table in solidworks can be used to ensure the correct thickness is chosen for your selected material along with the manufacturing properties as well.
Remember that we can always add information to an existing solidworks sheet metal gauge table by editing the excel spreadsheet including new gauge sizes and new bend radius values.
Sheet metal is one of the fundamental forms used in metalworking and it can be cut and bent into a variety of shapes countless everyday objects are fabricated from sheet metal.
You can access the sheet metal gauge bend table.
A gauge conversion chart can be used to determine the actual thickness of sheet metal in inches or millimeters.
The equivalent thicknesses differ for each gauge size standard which were developed based on the weight of the sheet for a given material.
Access the style and standard.
You use the sheet metal defaults dialog box to select a sheet metal rule.
Sheet metal gauge size chart gauge or gage sizes are numbers that indicate the thickness of a piece of sheet metal with a higher number referring to a thinner sheet.
Extremely thin sheets are considered foil or leaf and pieces thicker than 6 mm 0 25 in are considered.
We can also take one sheet metal gauge table and save as to create a new gauge table for a new material.
While creating the base flange from the base flange propertymanager.
You can also select a material type unfolding rule and sheet thickness that is different from the value specified in the sheet metal rule.
Sheet metal is metal formed by an industrial process into thin flat pieces.
For example 18 gauge steel according to a gauge conversion chart is 0 0478 inch or 1 214 millimeter.